Why does zero trust fail?
Summary
Contents
- 1 Summary
- 2 What are the challenges of zero trust
- 3 What is zero trust disadvantages
- 4 Does zero trust really work
- 5 What is the biggest challenge for zero trust
- 6 What are 3 of the more common challenges associated with implementing zero trust architectures
- 7 What is the major disadvantage of a trust
- 8 What are the pros and cons of zero trust
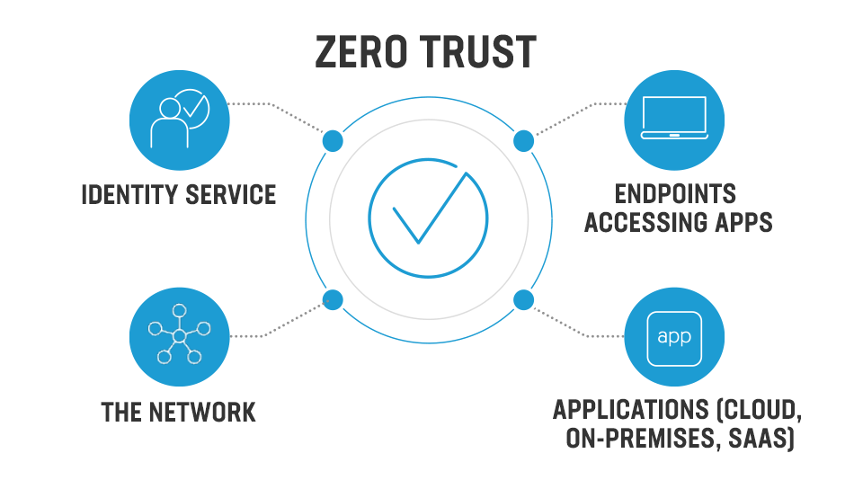
- 9 What are the 5 pillars of zero trust
- 10 How do you improve zero trust
- 11 What are the risks of zero trust architecture
- 12 What causes a trust to fail
- 13 What is a trust and why are they bad
- 14 How do you improve Zero Trust
This article explores the challenges and disadvantages of implementing a zero-trust security model, as well as its effectiveness and key considerations for improvement.
What are the challenges of zero trust
Here are the top five challenges of zero-trust security:
- Erosion of traditional control points
- Growth of business-led IT, a.k.a. Shadow SaaS
- Digital supply chain vulnerability
- Integrating security silos
- Single source of truth for risk
What is zero trust disadvantages
Zero Trust can take time and significant effort to set up effectively. Organizations may struggle with properly configuring existing tools and sometimes need to start the framework over again.
Does zero trust really work
Zero trust works well because every networked resource has its own multidimensional security requirements. It ensures that even authorized users cannot misuse their access.
What is the biggest challenge for zero trust
The biggest challenges of a zero-trust security model include piecemeal approach, lack of all-in-one products, legacy system adaptation, ongoing administration and maintenance, and potential hinderance of productivity.
What are 3 of the more common challenges associated with implementing zero trust architectures
The three common challenges associated with zero trust rollouts are productivity, change, and collaboration. Access to sensitive data can be hindered, impacting work progress.
What is the major disadvantage of a trust
The major disadvantages of trusts are their perceived irrevocability, loss of control over assets, and costs associated with creating and maintaining them.
What are the pros and cons of zero trust
The pros of zero trust include preventing attackers from gaining access to multiple resources at a time, while the cons involve the difficulty of achieving a complete transition to a zero-trust security model.
What are the 5 pillars of zero trust
The five pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are Identity, Devices, Network, Data, and Applications and Workloads.
How do you improve zero trust
To improve zero trust, organizations can follow a 5-step implementation strategy:
- Define the protect surface
- Map the transaction flows
- Architect a zero-trust network
- Create the zero-trust policy
- Monitor and maintain the network
What are the risks of zero trust architecture
The risks of zero-trust architecture include denial-of-service or network disruption, stolen credentials or insider threats, lack of visibility on the network, and storage of system and network information.
What causes a trust to fail
One of the most common reasons trusts fail is because grantors fail to fund them. Assets must be retitled into the name of the trust, which requires proper execution.
What is a trust and why are they bad
A trust helps an estate avoid taxes and probate, protects assets from creditors, and dictates inheritance terms. However, trusts require time and money to create and cannot be easily revoked.
How do you improve Zero Trust
To improve zero trust, organizations can follow a 5-step implementation strategy:
- Define the protect surface
- Map the transaction flows
- Architect a zero-trust network
- Create the zero-trust policy
- Monitor and maintain the network
What are the challenges of zero trust
Here are the top five challenges of zero-trust security:Erosion Of Traditional Control Points.Growth Of Business-Led IT, a.k.a. Shadow SaaS.Digital Supply Chain Vulnerability.Integrating Security Silos.Single Source Of Truth For Risk.Overcoming The Challenges Of Zero-Trust Security.
What is zero trust disadvantages
Con: Zero Trust can take time security teams don't have
Zero Trust takes time and significant effort to set up effectively. Sometimes, it may seem that an organization needs to start its framework over again, and organizations can struggle with properly configuring the tools they already use.
Does zero trust really work
Zero trust works so well because every networked resource has its own multidimensional security requirements. For example, if a malicious hacker sits down at an authorized logged-in machine with authorized software installed, the attacker themselves shouldn't be authorized.
What is the biggest challenge for zero trust
Top 6 challenges of a zero-trust security modelA piecemeal approach to zero-trust cybersecurity can create gaps.All-in-one zero-trust products don't exist.Legacy systems may not adapt to zero trust.Zero trust requires ongoing administration, maintenance.Zero trust can hinder productivity.
What are 3 of the more common challenges associated with implementing zero trust architectures
Access to sensitive data is part of the job, but if people change roles and find themselves locked out of pertinent files or applications, their work suffers. This scenario is precisely what leads to three common challenges with zero trust rollouts: productivity, change, and collaboration.
What is the biggest challenge for Zero Trust
Top 6 challenges of a zero-trust security modelA piecemeal approach to zero-trust cybersecurity can create gaps.All-in-one zero-trust products don't exist.Legacy systems may not adapt to zero trust.Zero trust requires ongoing administration, maintenance.Zero trust can hinder productivity.
What is the major disadvantage of a trust
The major disadvantages that are associated with trusts are their perceived irrevocability, the loss of control over assets that are put into trust and their costs. In fact trusts can be made revocable, but this generally has negative consequences in respect of tax, estate duty, asset protection and stamp duty.
What are the pros and cons of zero trust
Pro: Zero-trust systems prevent attackers from gaining access to multiple resources at a time. Con: It may not be possible to achieve a transition to a fully zero-trust security model.
What are the 5 pillars of zero trust
The five pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are: Identity; Devices; Network, Data, and Applications and Workloads.
How do you improve zero trust
A 5-step zero trust implementation strategyDefine the protect surface. Today's attack landscape is constantly changing.Map the transaction flows. Organizations must assess how their systems work when designing a network.Architect a zero trust network.Create the zero trust policy.Monitor and maintain the network.
What are the risks of zero trust architecture
Zero Trust Architecture Threats
denial-of-service or network disruption. stolen credentials/insider threat. visibility on the network. storage of system and network information.
What causes a trust to fail
One of the most common reasons trusts fail is because grantors fail to fund them. Once a trust is created, they must be funded, which means assets must be re-titled into the name of the trust. Many people fail to do this, or do not do this properly.
What is a trust and why are they bad
A trust helps an estate avoid taxes and probate. It can protect assets from creditors and dictate the terms of inheritance for beneficiaries. The disadvantages of trusts are that they require time and money to create, and they cannot be easily revoked.
How do you improve Zero Trust
A 5-step zero trust implementation strategyDefine the protect surface. Today's attack landscape is constantly changing.Map the transaction flows. Organizations must assess how their systems work when designing a network.Architect a zero trust network.Create the zero trust policy.Monitor and maintain the network.
What are the 7 layers of zero trust
Seven pillars of Zero Trust modelIdentity.Device.Network.Workload.Data.Visibility and analytics.Automation and orchestration.
What are the 7 core pillars of zero trust
by DriveLockWHAT IS A ZERO TRUST MODELTHE ZERO-TRUST MODEL FOR MORE EFFECTIVE SECURITY IS BASED ON THE FOLLOWING PILLARS. 2.1 ZERO TRUST NETWORKS. 2.2 ZERO TRUST WORKLOADS. 2.3 ZERO TRUST DEVICES. 2.4 ZERO TRUST DATA. 2.5 ZERO TRUST PEOPLE.VISIBILITY AND ANALYTICS.AUTOMATION AND ORCHESTRATION.
What is meant by failure of trust
Definition: Failure of trust refers to the invalidity of a trust due to a defect in the instrument creating it or because of its illegality or other legal impediment. Example: If a trust is created with an invalid or illegal purpose, it may be considered a failure of trust.
What are the six pillars of zero trust
The foundational pillars of Zero TrustWorkforce Security. Zero Trust provides a comprehensive approach to securing access across all the applications and environments, from any user, device, and location.Infrastructure Security.Device Security.Data Security.Workload Security.Process Security.Network Security.
What are the 4 goals of zero trust
The strategy unveiled in the fall outlined four high-level goals for achieving the DOD's vision for a zero trust architecture including cultural adoption, security and defense of DOD information systems, technology acceleration and zero trust enablement.
Which three 3 of practices are core principles of zero trust
Both human and non-human identities need strong authorization, connecting from either personal or corporate endpoints with compliant devices, requesting access based on strong policies grounded in Zero Trust principles of explicit verification, least-privilege access, and assumed breach.
What would cause a trust to fail
The purpose of a Trust is to manage the assets held in it. In order for the Trust to do it's job, the assets need to be in the Trust. If there are no assets in the Trust, then the Trust fails. Retitling the assets in the name of Trust is called funding the Trust.
What are the 5 pillars of Zero Trust
The five pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are: Identity; Devices; Network, Data, and Applications and Workloads.
What are the 7 pillars of Zero Trust
by DriveLockWHAT IS A ZERO TRUST MODELTHE ZERO-TRUST MODEL FOR MORE EFFECTIVE SECURITY IS BASED ON THE FOLLOWING PILLARS. 2.1 ZERO TRUST NETWORKS. 2.2 ZERO TRUST WORKLOADS. 2.3 ZERO TRUST DEVICES. 2.4 ZERO TRUST DATA. 2.5 ZERO TRUST PEOPLE.VISIBILITY AND ANALYTICS.AUTOMATION AND ORCHESTRATION.
What can damage trust
Mislead or obfuscate: Deliberately say things that aren't true or leave out pertinent facts in order to influence the opinions or feelings of others. 6. Question others' motives: Assume that people have ill-will or bad intentions.
What are the three core principles of Zero Trust
As business and technology continue to evolve, the three core principles of Zero Trust security remain consistent. Never trust. Always verify. Implement Zero Trust security for your business.