What is ZTNA in simple terms?
Summary
Contents
This article provides an overview of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and its key concepts. It highlights the differences between ZTNA and traditional VPNs, as well as the benefits of implementing a zero trust security model. The article also answers commonly asked questions about ZTNA, including its goals, functions, and examples. Overall, ZTNA is presented as a modern IT security solution that enhances remote access and reduces risks.
Main Thought
ZTNA is a revolutionary approach to IT security that prioritizes access control based on user authentication and trust, rather than network location.
Main Thought
Traditional VPNs provide direct access to a corporate LAN, while ZTNA only allows access to explicitly authorized applications and services, making it a more secure solution.
Key Points
1. The Concept of ZTNA
ZTNA provides secure remote access to an organization’s applications, data, and services based on clearly defined access control policies.
2. Zero Trust for Dummies
The zero trust model evaluates trust on a per-transaction basis rather than relying on network location or IP address.
3. ZTNA also known as SDP
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), also known as software-defined perimeter (SDP), implements and enforces an organization’s zero trust policy.
4. Goals of ZTNA
ZTNA aims to reduce third-party risk, hide sensitive applications, and ensure that only authorized users can access allowed applications.
5. ZTNA vs. VPN
Unlike VPNs, which provide tunneled access to a corporate LAN, ZTNA only permits access to explicitly authorized applications and services.
Questions and Answers
1. What is ZTNA?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is an IT security solution that provides secure remote access to an organization’s applications, data, and services based on clearly defined access control policies.
2. How is ZTNA different than VPN?
ZTNA only allows access to explicitly authorized applications and services, while VPNs provide direct access to a corporate LAN.
3. What are the goals of ZTNA?
The goals of ZTNA include reducing third-party risk, hiding sensitive applications, and ensuring that only authorized users can access allowed applications.
4. What is the difference between firewall and ZTNA?
While traditional firewalls work at a network level, ZTNA operates on an application level, enabling more granular access control.
5. What are the main concepts of zero trust?
The main concepts of zero trust include user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust, which are key components of a zero trust network.
6. What are the pillars of Zero Trust?
The pillars of Zero Trust include identity, devices, network, data, and applications/workloads, forming the foundation of a comprehensive security model.
7. How is ZTNA better than VPN?
ZTNA offers improved performance and reduced latency compared to VPNs, as it uses distributed gateways closer to the user and the resources they are accessing.
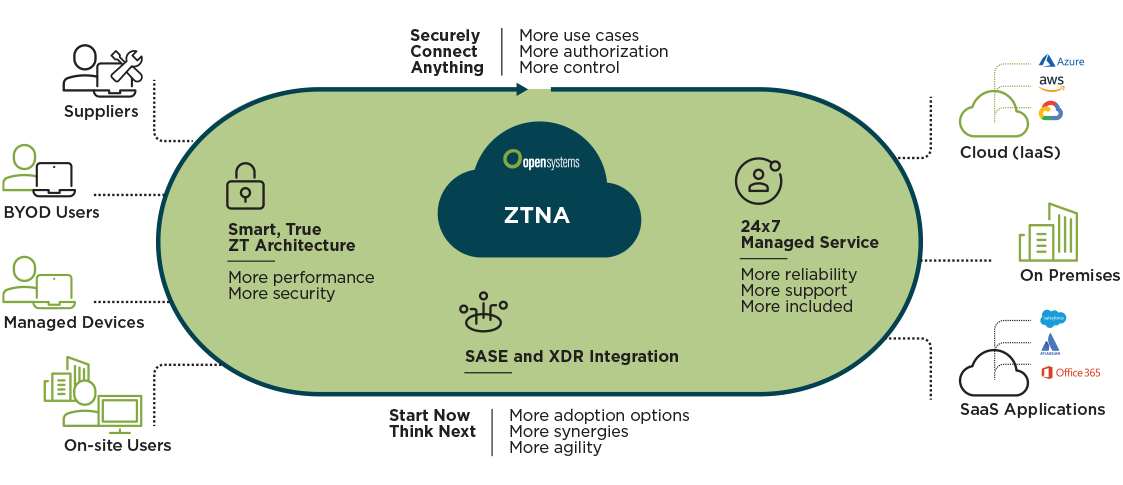
What is the concept of ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is an IT security solution that provides secure remote access to an organization's applications, data, and services based on clearly defined access control policies.
What is Zero Trust for dummies
The zero-trust model moves security away from implied trust that is based on the network location of a user or device. Instead, trust is evaluated on a per-transaction basis. With zero trust, your network location or IP address no longer conveys an implication of trust.
What is ZTNA also known as
Zero trust network access (ZTNA) – also known as software-defined perimeter (SDP) – solutions are designed to implement and enforce an organization's zero trust policy. Users attempting to connect to an organization's applications are only permitted to do so if they require that access to perform their duties.
What are the goals of ZTNA
Most third-party users receive overprivileged access, and they largely access applications using unmanaged devices, both of which introduce risks. ZTNA significantly reduces third-party risk by ensuring external users never gain access to the network and that only authorized users can access allowed applications.
Cached
How is ZTNA different than VPN
How Is ZTNA Different from VPN Unlike VPNs, which provide direct tunneled access to an endpoint on a corporate LAN, ZTNA provides access only to explicitly authorized applications and services.
What are two functions of ZTNA
Reduce third-party risk – Give contractors, vendors, and other third parties access to specific internal applications — and no more. Hide Sensitive Applications – Render applications “invisible” to unauthorized users and devices. ZTNA can significantly reduce the risk posed by insider threats.
What is an example of Zero Trust
The following are four clear examples of how zero trust can help protect the enterprise: Secure third-party access. Secure multi-cloud remote access. IoT security and visibility.
What are the 4 goals of Zero Trust
The strategy unveiled in the fall outlined four high-level goals for achieving the DOD's vision for a zero trust architecture including cultural adoption, security and defense of DOD information systems, technology acceleration and zero trust enablement.
What is the difference between firewall and ZTNA
Traditional firewalls work at a network level. Once you authenticate a remote user, they are free to access network resources. It can be difficult to limit the resources a user may access without complex firewall rules and convoluted network setups. ZTNA solutions instead work on an application level.
What are the three main concepts of zero trust
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
What are the 4 goals of zero trust
The strategy unveiled in the fall outlined four high-level goals for achieving the DOD's vision for a zero trust architecture including cultural adoption, security and defense of DOD information systems, technology acceleration and zero trust enablement.
What are the three main concepts of Zero Trust
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
What are the 5 pillars of Zero Trust
The five pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are: Identity; Devices; Network, Data, and Applications and Workloads.
How is ZTNA better than VPN
When it comes to latency as well, ZTNA has an edge over VPN as it does not require all traffic to be routed through a centralized gateway or server. Instead, ZTNA uses distributed gateways that are closer to the user and the resources they are accessing. This reduces latency and improves performance.
What are the 7 pillars of Zero Trust
by DriveLockWHAT IS A ZERO TRUST MODELTHE ZERO-TRUST MODEL FOR MORE EFFECTIVE SECURITY IS BASED ON THE FOLLOWING PILLARS. 2.1 ZERO TRUST NETWORKS. 2.2 ZERO TRUST WORKLOADS. 2.3 ZERO TRUST DEVICES. 2.4 ZERO TRUST DATA. 2.5 ZERO TRUST PEOPLE.VISIBILITY AND ANALYTICS.AUTOMATION AND ORCHESTRATION.
What are the 7 layers of zero trust
Seven pillars of Zero Trust modelIdentity.Device.Network.Workload.Data.Visibility and analytics.Automation and orchestration.
What are the three core principles of Zero Trust
As business and technology continue to evolve, the three core principles of Zero Trust security remain consistent. Never trust. Always verify. Implement Zero Trust security for your business.
What are the 5 basic tenets of DOD Zero Trust
Zero Trust is integrated into the five key cybersecurity functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Any attempts to deny, degrade, disrupt, deceive, or destroy information systems are mitigated.