What is the purpose of ZTNA?
Summary
Contents
- 1 Summary
- 2 Function of ZTNA
- 3 Benefits of ZTNA
- 4 Purpose of Zero Trust Architecture
- 5 Functions of ZTNA
- 6 ZTNA vs. VPN
- 7 Need for Zero Trust Security
- 8 Difference Between ZTNA and Firewall
- 9 Goals of Zero Trust
- 10 Concepts of Zero Trust
- 11 Zero Trust vs. VPN
- 12 Benefits of Fortinet ZTNA
- 13 Pillars of Zero Trust
This article discusses the concept of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and its importance in providing secure remote access to an organization’s applications, data, and services. It explains the benefits of ZTNA and compares it to traditional VPN solutions. The article also covers the key principles, goals, and components of a Zero Trust architecture.
Function of ZTNA
ZTNA is an IT security solution that allows organizations to establish secure remote access to their applications, data, and services. It does this by implementing access control policies based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This ensures that only authorized users and devices can access the organization’s resources.
Benefits of ZTNA
ZTNA offers several advantages over traditional VPN solutions. It provides better security by implementing strong authentication methods, network segmentation, and preventing lateral movement. ZTNA also enables organizations to quickly and securely stand up new applications, easily enroll or decommission users and devices, and gain insights into application status and usage.
Purpose of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is designed to protect modern environments and facilitate digital transformation. By following the principle of “never trust, always verify,” it enhances security by using strong authentication methods, network segmentation, and Layer 7 threat prevention. Zero Trust Architecture simplifies access control and prevents unauthorized lateral movement.
Functions of ZTNA
ZTNA serves multiple functions, including reducing third-party risk by providing specific access to internal applications. It also allows organizations to hide sensitive applications from unauthorized users and devices. ZTNA significantly mitigates the risk posed by insider threats.
ZTNA vs. VPN
ZTNA offers several advantages over traditional VPNs. It provides faster access to resources by utilizing distributed gateways closer to the user. This reduces latency and improves performance. Additionally, ZTNA implements device posture checks, identity provider integrations, and multi-factor authentication to create a protective barrier against potential attacks.
Need for Zero Trust Security
A well-executed zero trust strategy allows organizations to more precisely control access, even for employees with elevated privileges. By granting authenticated access based on trust dimensions, businesses can significantly reduce the potential risks associated with unrestricted network access.
Difference Between ZTNA and Firewall
The main difference between ZTNA and traditional firewalls lies in their approach. While firewalls primarily work at a network level and necessitate complex rules and setups to control resource access, ZTNA operates on the application level. ZTNA includes device posture checks, identity verification, and multi-factor authentication to ensure secure access to applications.
Goals of Zero Trust
The goals of Zero Trust include cultural adoption, the security and defense of information systems, technology acceleration, and enabling Zero Trust architecture. These goals are aimed at achieving a secure and trusted environment for organizations.
Concepts of Zero Trust
Zero Trust networks revolve around three key components: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust. These components form the foundation of a Zero Trust architecture.
Zero Trust vs. VPN
Zero Trust strategies are designed to meet modern needs for visibility, control, and secure remote work. While VPN services offer connectivity, Zero Trust provides additional benefits such as improved speed, performance, and security.
Benefits of Fortinet ZTNA
The Fortinet Approach to ZTNA offers several technical benefits. These include enabling true work from anywhere, bringing zero trust to remote access, providing consistent application access policies for users on and off the network, and granting users granular access to applications.
Pillars of Zero Trust
The five pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are Identity, Devices, Network, Data, and Applications. These pillars form the framework for implementing Zero Trust principles and ensuring comprehensive security.
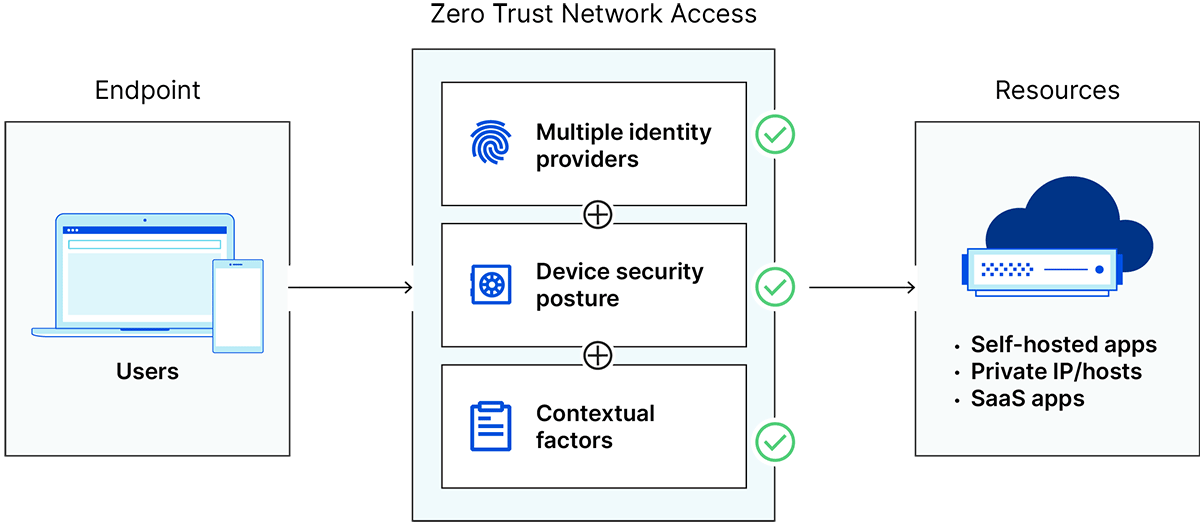
What is the function of ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is an IT security solution that provides secure remote access to an organization's applications, data, and services based on clearly defined access control policies.
What is the benefit of ZTNA
ZTNA enables better security and more agility in quickly changing environments with users coming and going. Stand-up new applications quickly and securely, easily enroll or decommission users and devices, and get insights into application status and usage.
What is the purpose of zero trust architecture
Rooted in the principle of “never trust, always verify,” Zero Trust is designed to protect modern environments and enable digital transformation by using strong authentication methods, leveraging network segmentation, preventing lateral movement, providing Layer 7 threat prevention, and simplifying granular, “least …
What are two functions of ZTNA
Reduce third-party risk – Give contractors, vendors, and other third parties access to specific internal applications — and no more. Hide Sensitive Applications – Render applications “invisible” to unauthorized users and devices. ZTNA can significantly reduce the risk posed by insider threats.
Cached
Why is ZTNA better than VPN
When it comes to latency as well, ZTNA has an edge over VPN as it does not require all traffic to be routed through a centralized gateway or server. Instead, ZTNA uses distributed gateways that are closer to the user and the resources they are accessing. This reduces latency and improves performance.
Why do we need zero trust security
Even employees perform specialized functions and therefore do not need complete network access. A well-executed zero trust strategy allows authenticated access based on key dimensions of trust. This enables businesses to more precisely control access, even to those with elevated privileges.
What is the difference between ZTNA and firewall
Physical firewalls don't check for device posture security. With ZTNA, device posture check is implemented along with Identity Provider integrations and Multi-Factor Authentication, creating a protective barrier from potential attacks.
What are the 4 goals of zero trust
The strategy unveiled in the fall outlined four high-level goals for achieving the DOD's vision for a zero trust architecture including cultural adoption, security and defense of DOD information systems, technology acceleration and zero trust enablement.
What are the three main concepts of zero trust
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
What is the difference between firewall and ZTNA
Traditional firewalls work at a network level. Once you authenticate a remote user, they are free to access network resources. It can be difficult to limit the resources a user may access without complex firewall rules and convoluted network setups. ZTNA solutions instead work on an application level.
How will zero trust replace VPN
Replace VPN with Zero Trust Strategy
While VPN services do offer a level of connectivity, zero trust is specifically designed to meet modern needs for visibility and control as well as critical business demands such as remote work, speed, performance, security and more.
What are the benefits of Fortinet ZTNA
These Are the Top Technical Benefits of the Fortinet Approach to ZTNA:Enables true work from anywhere.Brings zero trust to remote access.Provides consistent application access policies for users on and off the network.Gives users granular access to applications.
What are the three main concepts of Zero Trust
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
What are the 5 pillars of Zero Trust
The five pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are: Identity; Devices; Network, Data, and Applications and Workloads.
What is the key principle of zero trust
What is Zero Trust Zero trust is a modern security strategy based on the principle: never trust, always verify. Instead of assuming everything behind the corporate firewall is safe, the Zero Trust model assumes breach and verifies each request as though it originates from an open network.
What is the difference between ZTNA and VPN
How Is ZTNA Different from VPN Unlike VPNs, which provide direct tunneled access to an endpoint on a corporate LAN, ZTNA provides access only to explicitly authorized applications and services.
What are the 4 goals of Zero Trust
The strategy unveiled in the fall outlined four high-level goals for achieving the DOD's vision for a zero trust architecture including cultural adoption, security and defense of DOD information systems, technology acceleration and zero trust enablement.
What are the 3 principles of zero trust
Zero Trust seeks to address the following key principles based on the NIST guidelines: Continuous verification. Always verify access, all the time, for all resources. Limit the “blast radius.”
Why zero trust is better than VPN
That's because VPNs work by routing all traffic through a data center to then be decrypted. But ultimately this process can take time and result in slow-moving protection. Because zero trust is primarily cloud-based, connections are quick and efficient. (Also read: The Best Practices for Managing Cloud Applications.)
What are the disadvantages of zero trust network
It can be expensive and complex to implement, requiring significant changes to the organization's network infrastructure and security policies. Zero-trust security can also increase the risk of user frustration and reduce productivity, as users may need to authenticate multiple times to access different resources.
What is the difference between zero trust and ZTNA
While zero trust is the overarching framework, ZTNA is a subset of zero trust that deals with identity and access management for users who are accessing an organization's applications.
What are the pros and cons of zero trust
The Pros and Cons of Zero Trust SecurityCon: More applications, devices, and users to monitor.Pro: Reduce susceptibility to insider attacks.Con: Zero Trust can take time security teams don't have.Pro: Discovering user identity and permissions.Con: Data, data, everywhere…Pro: Narrowing the attack surface.
What are the principles of ZTNA
The ZTNA model is a mix of the principle of least privilege, software-defined perimeters, and advanced security tools and policies. The two main ZTNA architectures are endpoint-initiated (using an agent on each user's device) and service-initiated (using the cloud).
What are the three core principles of Zero Trust
As business and technology continue to evolve, the three core principles of Zero Trust security remain consistent. Never trust. Always verify. Implement Zero Trust security for your business.
What are the three main elements of a zero trust implementation
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.