What is the difference between VPN and zero trust network?
Summary
Contents
- 1 Summary
- 2 Key Points
- 3 1. Zero Trust versus VPN
- 4 2. Do I need a VPN with zero trust?
- 5 3. What is a zero trust network?
- 6 4. What is another name for zero trust?
- 7 5. Why is zero trust better than VPN?
- 8 6. Why is VPN better than zero trust?
- 9 7. What is an example of a zero trust network?
- 10 8. What are the disadvantages of zero trust networks?
- 11 9. What is replacing VPN?
- 12 10. What is the most trusted VPN?
- 13 Questions and Answers
- 13.1 1. What is the difference between VPN and zero trust network?
- 13.2 2. Do I need a VPN with zero trust?
- 13.3 3. What is a zero trust network?
- 13.4 4. What is another name for zero trust?
- 13.5 5. Why is zero trust better than VPN?
- 13.6 6. What is an example of a zero trust network?
- 13.7 7. Why is VPN better than zero trust?
In this article, I will discuss the difference between VPN and zero trust networks, as well as answer some commonly asked questions related to the topic.
Key Points
1. Zero Trust versus VPN
While VPNs have been widely used for remote access, zero trust networks are a newer concept that aims to provide more secure connectivity. Zero trust networks implement principles that assume there are attackers both inside and outside the network, requiring verification of user and device identities.
2. Do I need a VPN with zero trust?
While VPNs can offer secure remote access, they do not provide the same capabilities as a zero trust network. Zero trust networks go beyond simply granting access and focus on continuously verifying user and device identity to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
3. What is a zero trust network?
A zero trust network is a security approach that eliminates the concept of trust in traditional network architectures. The philosophy assumes that no users or machines should be automatically trusted, and access is granted based on continuous verification of identity and security.
4. What is another name for zero trust?
Zero trust networks are sometimes referred to as “adaptive authentication” due to the emphasis on continuously verifying user identity and privileges.
5. Why is zero trust better than VPN?
Zero trust networks offer more efficient and secure connectivity compared to VPNs. VPNs route all traffic through a centralized data center, leading to potential delays, whereas zero trust networks are cloud-based and enable quick and efficient connections.
6. Why is VPN better than zero trust?
VPNs can have an advantage over zero trust networks when it comes to latency. VPNs do not require all traffic to be routed through a centralized gateway, resulting in reduced latency and improved performance.
7. What is an example of a zero trust network?
One example of a zero trust policy is multifactor authentication, where users are required to perform multiple authentication methods to access resources. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
8. What are the disadvantages of zero trust networks?
Implementing zero trust networks can be complex and expensive, requiring significant changes to network infrastructure and security policies. It can also result in user frustration and reduced productivity due to the need for multiple authentications.
9. What is replacing VPN?
Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) are two alternatives to traditional VPNs. SD-WAN provides more efficient routing of encrypted traffic, while SASE combines network security and wide-area networking capabilities.
10. What is the most trusted VPN?
ExpressVPN is a highly regarded VPN service, known for its dedication to privacy and fast speeds. It has consistently received positive reviews and awards.
Questions and Answers
1. What is the difference between VPN and zero trust network?
The difference lies in their approach to security. While VPNs focus on secure remote access, zero trust networks prioritize continuous verification of user and device identities to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Do I need a VPN with zero trust?
No, zero trust networks offer secure connectivity on their own, eliminating the need for a VPN. They provide more robust security measures, including continuous identity verification.
3. What is a zero trust network?
A zero trust network is a security approach that assumes there are attackers both inside and outside the network. It requires continuous verification of user and device identity to grant access.
4. What is another name for zero trust?
Zero trust networks are sometimes referred to as “adaptive authentication” due to their focus on continuously verifying user identity and privileges.
5. Why is zero trust better than VPN?
Zero trust networks offer more efficient and secure connectivity compared to VPNs. They eliminate the need for routing all traffic through a centralized data center, resulting in quicker and more efficient connections.
6. What is an example of a zero trust network?
One example is the use of multifactor authentication, where users must perform multiple authentication methods to gain access. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
7. Why is VPN better than zero trust?
VPNs may have an advantage in terms of latency, as they do not require all traffic to be routed through a centralized gateway. This leads to reduced latency and improved performance.
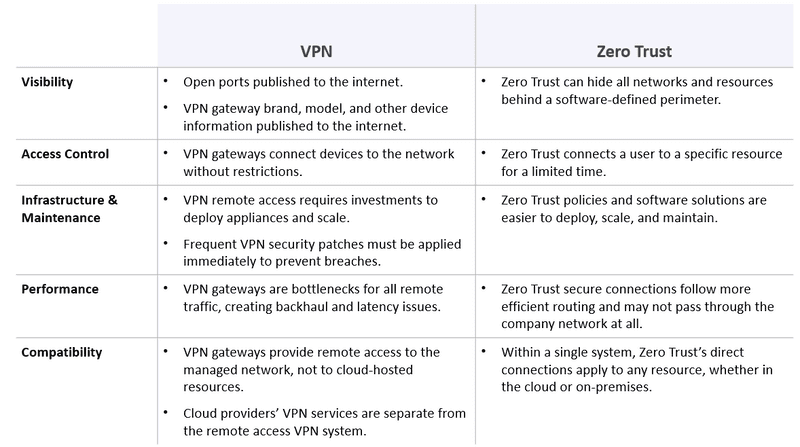
How is zero trust different from VPN
While VPNs have historically had a place in most network security plans, zero trust is a relatively new concept that aims to fill in the security gaps traditional security approaches miss. An SDP is a network architecture that implements zero-trust principles to provide more secure remote access than VPNs.
Do I need a VPN with zero trust
VPNs are a well-established remote access solution, and many organizations turned to them to support their remote employees. However, while VPNs offer employees secure remote access to the corporate network, they fail to provide crucial capabilities for a zero trust deployment.
What is a zero trust network
The philosophy behind a Zero Trust network assumes that there are attackers both within and outside of the network, so no users or machines should be automatically trusted. Zero Trust verifies user identity and privileges as well as device identity and security.
What is another name for zero trust
This hybrid version of Zero Trust may also be referred to as “Adaptive Authentication.”
Why is Zero Trust better than VPN
That's because VPNs work by routing all traffic through a data center to then be decrypted. But ultimately this process can take time and result in slow-moving protection. Because zero trust is primarily cloud-based, connections are quick and efficient. (Also read: The Best Practices for Managing Cloud Applications.)
Why is VPN better than ZTNA
When it comes to latency as well, ZTNA has an edge over VPN as it does not require all traffic to be routed through a centralized gateway or server. Instead, ZTNA uses distributed gateways that are closer to the user and the resources they are accessing. This reduces latency and improves performance.
What is an example of a zero trust network
One of the most effective Zero Trust policies is multifactor authentication. Requiring that every user perform two or more forms of authentication (such as using a PIN on a known device) every time they sign in significantly decreases the risk that a bad actor with stolen credentials will gain access.
What is the disadvantage of zero trust
Adopting Zero Trust can therefore be a labor intensive process. IT teams need to assess every device and application. Teams must create profiles for every user, with no exceptions. Meticulous planning can also lead to a secondary risk of moving too slowly.
What is the disadvantage of Zero Trust
Adopting Zero Trust can therefore be a labor intensive process. IT teams need to assess every device and application. Teams must create profiles for every user, with no exceptions. Meticulous planning can also lead to a secondary risk of moving too slowly.
What is an example of Zero Trust
One of the most effective Zero Trust policies is multifactor authentication. Requiring that every user perform two or more forms of authentication (such as using a PIN on a known device) every time they sign in significantly decreases the risk that a bad actor with stolen credentials will gain access.
What are the disadvantages of zero trust network
It can be expensive and complex to implement, requiring significant changes to the organization's network infrastructure and security policies. Zero-trust security can also increase the risk of user frustration and reduce productivity, as users may need to authenticate multiple times to access different resources.
What is replacing VPN
Two of the most common choices are software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). SD-WAN is designed to be a more efficient alternative to the VPN. Instead of implementing point-to-point connectivity, SD-WAN provides optimal routing of encrypted traffic between a network of SD-WAN appliances.
What is the number one trusted VPN
ExpressVPN retained CNET Editors' Choice Award for best overall VPN after its 2023 review. It maintains its position among other virtual private network services thanks to its dedication to privacy and strong speeds.
What is zero trust for dummies
The zero-trust model moves security away from implied trust that is based on the network location of a user or device. Instead, trust is evaluated on a per-transaction basis. With zero trust, your network location or IP address no longer conveys an implication of trust.
What is the biggest challenge for zero trust
Top 6 challenges of a zero-trust security modelA piecemeal approach to zero-trust cybersecurity can create gaps.All-in-one zero-trust products don't exist.Legacy systems may not adapt to zero trust.Zero trust requires ongoing administration, maintenance.Zero trust can hinder productivity.
Is Zero Trust good or bad
By enforcing strict access controls, continuously verifying trust, and segmenting the network, zero trust helps prevent lateral movement by attackers, limits the scope of potential breaches, and minimizes the impact of compromised credentials.
What is Zero Trust for dummies
The zero-trust model moves security away from implied trust that is based on the network location of a user or device. Instead, trust is evaluated on a per-transaction basis. With zero trust, your network location or IP address no longer conveys an implication of trust.
Is zero trust good or bad
By enforcing strict access controls, continuously verifying trust, and segmenting the network, zero trust helps prevent lateral movement by attackers, limits the scope of potential breaches, and minimizes the impact of compromised credentials.
When I shouldn’t use VPN
Why shouldn't I use a VPNA VPN might reduce your connection speed even if your internet service provider isn't throttling your speed;Using a VPN on mobile will increase your mobile data usage;Using a VPN is considered an offense in some countries, and you can get fined or even be incarcerated for it.
Why VPN is outdated
VPNs first arrived in the '90s, but like most 1990s tech, they're not equipped to protect against modern threats. It doesn't integrate well with other systems, and its best feature — private access to corporate systems — is now better accomplished with zero-trust architecture.
Do you really need a VPN
VPN use is important for online privacy whenever you're logging into the internet from a public spot because cyber snoops could track your online activity when you are using public Wi-Fi, whether it's on your computer or your mobile device.
How much does a VPN cost per month
A good VPN often costs around $5 to $10 per month. This pricing could vary depending on each VPN service provider, the types of features you want included, and the subscription plan you choose. Choosing an annual plan that you pay for upfront typically reduces the overall cost.
Does ZTNA replace VPN
ZTNA provides a more seamless and user-friendly experience than VPNs. Users do not have to install any software or configure any settings, and they can access the resources they need from anywhere and any device. ZTNA also provides better performance and reliability, which can improve user productivity.
What are the challenges of zero trust
Here are the top five challenges of zero-trust security:Erosion Of Traditional Control Points.Growth Of Business-Led IT, a.k.a. Shadow SaaS.Digital Supply Chain Vulnerability.Integrating Security Silos.Single Source Of Truth For Risk.Overcoming The Challenges Of Zero-Trust Security.
What are the downsides of zero trust
5. Zero Trust Can Be Costly. Another disadvantage of Zero Trust is that it can be costly to implement. This is because it requires more manpower and additional security measures — such as multi-factor authentication — which can add to the overall cost of the system.