What are Tier 3 schools in the US?
My Personal Experience with Tier 3 Schools
Summary: In this article, I will share my personal experience with Tier 3 schools and their importance in the education system.
Main Thought: Tier 3 schools play a crucial role in providing support and intervention to students who require more individualized attention.
Key Points:
1. Tier 3 schools provide intensive support: At Tier 3, students receive personalized and intensive support to improve their behavioral and academic outcomes. This level of support is especially beneficial for students with developmental disabilities, autism, emotional and behavioral disorders, and even those without a diagnostic label.
2. Differentiating Tier 1, 2, and 3 colleges: Tier 2 universities are considered good quality institutions, while Tier 3 universities are perceived as of lower quality than the other tiers. Understanding these differences can help students make informed choices about their higher education.
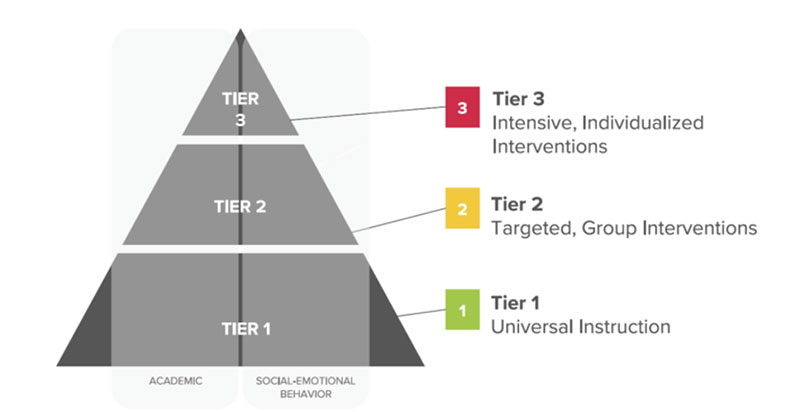
3. Definition of Tier 1, 2, and 3 education: Within the education system, Tier 1 refers to universal or core instruction, Tier 2 represents targeted or strategic instruction/intervention, and Tier 3 denotes intensive instruction/intervention. This tiered approach ensures that students receive the appropriate level of support based on their individual needs.
4. Differentiation between Tier 2 and Tier 3 in education: While both tiers provide additional support beyond the core instruction, Tier 2 focuses on small-group targeted support, whereas Tier 3 offers even more intensity through daily one-on-one tutoring. Reducing the number of students in learning groups allows for more personalized attention.
5. The importance of Tier 3 interventions: Tier 3 interventions play a significant role in addressing the specific needs of students who require intensive individualized instruction. These interventions aim to support students in developing necessary skills and achieving academic success.
6. Tier 3 in the context of criminal offenses: In the legal system, Tier 3 offenses refer to sex offenses that are punishable by more than one year in jail. Offenders with prior convictions for Tier 2 offenses or those who have previously become Tier 2 sex offenders fall under this category.
7. Understanding Tier 4 universities: Tier 4 universities include smaller private schools or state-sponsored research institutions that are generally not as well-known as Tier 1 and Tier 2 institutions. These universities often have higher admissions rates and may serve as target or safety schools for students.
8. Distinguishing UCLA as a Tier 1 or Tier 2 university: UCLA is classified as a Tier 1 university, along with UC Berkeley. These universities are highly selective and widely regarded as top-tier institutions within the University of California system.
9. Tier 4 in the context of education initiatives: Tier 4 in education refers to practices with a well-defined logic model or theory of action, supported by research, and undergoing evaluation to determine their effectiveness. It represents a stage where interventions are being actively analyzed.
10. Difference between Tier 1, 2, 3, and 4 in education: The differences between these tiers lie in the level of redundancy and infrastructure resilience. Tier 1 offers no redundancy, Tier 2 has partial redundancy in critical systems, Tier 3 includes dual redundancy, and Tier 4 possesses fully redundant infrastructure.
11. Understanding the supplier tiers: Supplier tiers in business operations indicate the level of proximity to the final product. Tier 1 suppliers are direct suppliers, Tier 2 suppliers are suppliers to Tier 1, and Tier 3 suppliers are suppliers to Tier 2. The tiers can extend further depending on the supply chain.
Questions and Answers:
1. Question: What are Tier 3 schools in the US?
Answer: Tier 3 schools provide intensive support to students with diverse needs, including developmental disabilities, autism, emotional and behavioral disorders, and students without a specific diagnostic label.
2. Question: What is the difference between Tier 1, 2, and 3 colleges in the US?
Answer: Tier 1 colleges are highly selective and prestigious institutions, Tier 2 colleges are considered good quality but not as highly ranked, and Tier 3 colleges are generally of lower quality compared to the other tiers.
3. Question: What is Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 education?
Answer: Tier 1 represents core instruction for all students, Tier 2 focuses on targeted instruction/intervention, and Tier 3 provides intensive instruction/intervention for students with specialized needs.
4. Question: What is the difference between Tier 2 and Tier 3 in education?
Answer: Tier 2 offers small-group targeted support, while Tier 3 provides even more intensity through daily one-on-one tutoring, ensuring personalized attention for students.
5. Question: What does Tier 3 mean in the context of legal offenses?
Answer: Tier 3 offenses refer to sex offenses that carry a punishment of more than one year in jail, applicable to offenders with prior convictions for Tier 2 offenses or who have previously become Tier 2 sex offenders.
6. Question: What is a Tier 4 university?
Answer: Tier 4 universities encompass smaller private schools or state-sponsored research institutions that may not be as renowned as Tier 1 and Tier 2 universities. They often have higher admissions rates and serve as target or safety schools.
7. Question: Is UCLA considered a Tier 1 or Tier 2 university?
Answer: UCLA is classified as a Tier 1 university, along with UC Berkeley. These universities are highly selective and widely regarded as top-tier institutions within the University of California system.
8. Question: Is there a Tier 4 in education?
Answer: Yes, Tier 4 in education is a categorization that represents practices undergoing evaluation to determine their effectiveness. They have a well-defined logic model or theory of action and are supported by research.
9. Question: What does Tier 4 mean in the context of education?
Answer: In education, Tier 4 refers to smaller private schools or state-sponsored research universities that may not be as well-known as Tier 1 and Tier 2 institutions. These schools typically have higher admissions rates.
10. Question: What is a Tier 1 school?
Answer: Tier 1 schools typically include major private research universities known for their academic excellence and high prestige. They often have larger campuses, graduate schools, and medium-large student populations.
11. Question: What is the difference between Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4 in terms of data centers?
Answer: The difference lies in the redundancy and infrastructure resilience. Tier 1 offers no redundancy, Tier 2 has partial redundancy in key systems, Tier 3 includes dual redundancy, and Tier 4 provides fully redundant infrastructure.
12. Question: What is the difference between Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 suppliers?
Answer: Tier 1 suppliers directly supply the final product, while Tier 2 suppliers are suppliers or subcontractors for Tier 1 suppliers. Tier 3 suppliers are suppliers or subcontractors for Tier 2 suppliers, with the tiers potentially extending further.
What is tier 3 in school
At Tier 3, these students receive more intensive, individualized support to improve their behavioral and academic outcomes. Tier 3 strategies work for students with developmental disabilities, autism, emotional and behavioral disorders, and students with no diagnostic label at all.
What are Tier 1 2 3 colleges in us
Tier 2 universities are usually considered to be good quality institutions, but not as highly ranked as tier 1 universities. Tier 3 universities are generally considered to be of lower quality than the other two tiers.
What is Tier 1 Tier 2 and Tier 3 education
For this reason, school-specific terms for these levels of support were developed: Tier 1 = Universal or core instruction. Tier 2 = Targeted or strategic instruction/intervention. Tier 3 = Intensive instruction/intervention.
What is Tier 2 and Tier 3 in education
Reducing the number of students in learning groups provides them more opportunities to practice new skills and respond to what they are learning. Tier 2 provides instruction to small groups of three to four students, while Tier 3 offers even more intensity through daily one-on-one tutoring.
What’s the difference between Tier 2 and Tier 3
Get an overview of how schools can organize their Tier 2 and Tier 3 interventions within an MTSS/RTI framework. Tier 2 provides small-group targeted support and Tier 3 provides intensive individualized intervention.
What does Tier 3 mean
Recidivism and Felonies. Any sex offense that is punishable by more than one year in jail where the offender has at least one prior conviction for a Tier 2 sex offense, or has previously become a Tier 2 sex offender, is a “Tier 3” offense.
What is a Tier 4 university
Tier 4. These schools are not famous, and include many smaller private schools or state sponsored research universities. They have admissions rates above 35%, and may be treated as target or safety schools by most students.
Is UCLA tier 1 or Tier 2
Tier 1: UC Berkeley and UCLA
They're the most selective and generally the most well-regarded of the UC schools.
Is there a Tier 4 in education
Tier 4 – Demonstrates a Rationale: practices that have a well-defined logic model or theory of action, are supported by research, and have some effort underway by an SEA, LEA, or outside research organization to determine their effectiveness.
What does Tier 4 mean in education
Tier 4. These schools are not famous, and include many smaller private schools or state sponsored research universities. They have admissions rates above 35%, and may be treated as target or safety schools by most students.
What is a tier 1 school
Tier 1 is comprised of major private research universities, including MIT, UChicago, Stanford, John Hopkins, Northwestern, California Institute of Technology, Duke, Vanderbilt, and Rice (amongst many others). The campuses are likely to be quite large and include graduate schools and a medium-large student population.
What is tier 1 vs Tier 2 vs Tier 3 vs Tier 4
As a general rule, the difference between data center tiers is that tier 1 offers no redundancy of any critical system, tier 2 has partial redundancy in their electrical & HVAC systems, tier 3 contains dual redundancy for power & cooling equipment, and tier 4 possesses fully redundant infrastructure.
What’s the difference between tier 1 2 and 3
Tier 1 Suppliers: These are direct suppliers of the final product. Tier 2 suppliers: These are suppliers or subcontractors for your tier 1 suppliers. Tier 3 suppliers: These are suppliers or subcontractors for your tier 2 suppliers. These tiers can extend longer than three.
What’s a Tier 1 university
Tier 1 is comprised of major private research universities, including MIT, UChicago, Stanford, John Hopkins, Northwestern, California Institute of Technology, Duke, Vanderbilt, and Rice (amongst many others). The campuses are likely to be quite large and include graduate schools and a medium-large student population.
What is Tier 2 university in USA
Tier 2 colleges
They often have acceptance rates of less than 20%. Tier 2 colleges have equal academic and extracurricular expectations, but the number of students that apply is fewer, which means that each eligible student has a better chance of being accepted. Tier 2 colleges are also elite institutions.
What tier is NYU
Not to mention, NYU is a tier-two school. While tier-one schools contain the Ivies, tier-two schools are slightly less competitive. However, these are still elite universities. Tier-two schools are reach schools for many students, with acceptance rates below 20%.
Is Texas A&M a Tier 1 school
Texas A&M University is the sixth largest university in the United States and the largest university in Texas. As a Tier 1 research institution, our university features nationally ranked programs in engineering, agriculture and life sciences, chemistry, architecture and business. Learn more.
What is a Tier 1 school
Tier 1 is comprised of major private research universities, including MIT, UChicago, Stanford, John Hopkins, Northwestern, California Institute of Technology, Duke, Vanderbilt, and Rice (amongst many others). The campuses are likely to be quite large and include graduate schools and a medium-large student population.
What does Tier 5 school mean
Tier 5. These are safety schools for almost all applicants, and will admit most of the students who apply to them. These include local colleges, and the less prestigious branches of state university systems. While these schools are not “bad,” they are generally considered less prestigious.
What is tier 2 in school
Tier 2. The secondary level of interventions in schools (now commonly called Tier 2) focuses on specific students who show initial signs or symptoms of difficulty. Data from these students is then used to provide targeted interventions to those "at-risk" students based on their specific needs and symptoms.
Is Harvard a Tier 1 school
Tier 1 schools include: Stanford, Harvard, Princeton, Yale, MIT, UChicago, Caltech, Columbia, Brown, Northwestern, The University of Pennsylvania, Dartmouth, Duke, Vanderbilt, Cornell, Johns Hopkins, and Rice.
What is the difference between Tier 1 and Tier 2 schools
Tier 1 instruction is standards-driven, focusing on students' broad skills and generalizing to a learning target. In contrast, Tier 2 intervention targets a specific skill deficit that has been identified through assessment. Instruction and intervention targets this specific skill.
What is Tier 1 colleges in USA
Other Definitions for Tier 1 Universities
| Name | Type | Top American Research University |
|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | Private | 1 |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | Private | 1 |
| Yale University | Private | 5 |
| Stanford University | Private | 1 |
Is UCLA Tier 1 or Tier 2
Tier 1: UC Berkeley and UCLA
They're the most selective and generally the most well-regarded of the UC schools.
What tier is UCLA
University of California, Los Angeles is ranked #15 out of 439 National Universities. Schools are ranked according to their performance across a set of widely accepted indicators of excellence. Read more about how we rank schools.